Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Beck’s Cognitive Theory of Depression: Incorporating Theory
Description
For the proposed research, the PICO question that guides the study is as follows: In young adults aged 30 to 35 years-old (P), is using a screening tool for depression (I), in comparison to the usual standard of care (C), more accurate in detecting depression (O). This PICO question helps in finding out whether or not there is sufficient evidence to support screening young adults aged 30 years to 35 years for depression with the use of a suitable screening tool.
Utilization in Supporting Solution
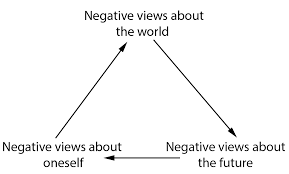
The theory that could be utilized in supporting the proposed solution is Beck’s Cognitive Theory of Depression. Beck identified 3 main components or mechanisms which are responsible for depression. These include: (i) negative self schemas; (ii) the cognitive triad; and (iii) errors in logic, that is, faulty processing of information (Abela & D’Allesandro, 2012). The cognitive triad are 3 types of negative thinking which are common in people who have depression: that is negative thoughts concerning the future, the world, and the self.
These negative thoughts are automatic in individuals with depression since they occur impulsively. Beck pointed out that people who are prone to depression develop a negative self-schema. Such an individual possesses various expectations and beliefs regarding himself or herself which are pessimistic and negative. Individuals who have negative self schemas are inclined to making logical errors in their thinking. They are also inclined to focusing mainly on particular facets of a situation whilst disregarding other information that is equally pertinent (Abela & D’Allesandro, 2012).
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
The rationale for selecting this theory is that this theory helps to describe what really is central to depression; that is, the main cause of depression. According to Beck, the cognitive symptoms of depression in fact precede the mood and affective symptoms of depression, and not the other way round. What is central to depression, as Beck pointed out, are the negative thoughts and not low reinforcement rates or hormonal changes as other theorists had suggested (Abela & D’Allesandro, 2012).
This theory works to support the proposed solution in that using depression screening tools, the researcher will be able to determine more accurately the main cause of depression amongst young adults in the United States. In other words, using appropriate screening tools for depression, it would be possible to detect the negative thoughts in people aged 30-35 in the United States considering that negative thoughts are central to depression as per Beck’s Cognitive Theory of Depression.
Incorporation
The theory would be incorporated into the project by using screening tools for depression which are in line with Beck’s Cognitive Theory of Depression. One particular screening tool that would be used is the Beck Depression Inventory-II (BDI-II) which was developed by the same theorist who conceptualized Beck’s Cognitive Theory of Depression. The BDI-II screening tool for depression would be utilized to detect depression among 30-35 year-old young adults and it would be compared with the usual standard of care currently being practiced in the country.
In essence, using Beck’s Cognitive Theory of Depression, the negative thoughts of people would be carefully monitored using Beck Depression Inventory. It is expected that depressed people negatively misunderstand information and experiences, as they limit their focus to the negative facets of a situation, therefore feeling hopeless regarding the future (Abela & D’Allesandro, 2012). Using Beck’s Cognitive Theory of Depression in the project, a direct correlation is postulated between severity of symptoms of depression and negative thoughts.
References
Abela, J. R. Z., & D’Allesandro, D. U. (2012). Beck’s cognitive theory of depression: The diathesis-stress and causal mediation components. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 41, 111-128.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here