Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Health and Safety in the Health and Social Care Workplace
A Case Study of Silver Meadows
Introduction
Health and safety is always a crucial aspect that poses a concern to everyone with regards to day-to-day affairs. In health and social care settings, especially care homes for the elderly health and safety remains a fundamental consideration for all law enforcement agencies as well as practitioners. This makes the importance of continuous monitoring in addition to reviewing of health as well as legislations and safety policies’ implementation for health as well as social care workplace undisputable and this has been succinctly discussed and explained in this assignment.
According to Graham & Steven (2008) this is attributable to the fact that, good health and safety of care home residents is the key to their happiness something which has made the management and staff of home care workplaces to be cautious enough in managing health and safety issues. As a result, health protective agencies have been emphasizing on the implementation of appropriate policies, systems, and procedures for health and safety in all health as well as social care settings to alleviate hazards.
The context of this assignment will provide a clear view of policies, systems, and practices and their effect in the promotion of safety in health and social care home in the perspective of Silver Meadows Care Home. From the perspective of health and social care home, employees, patients and their relatives or visitors ought to be protected from hazards. Therefore, in health and social care working environment, the management, staff as well as individual patients have the right to participate in implementing health and safety plans for the benefit of all those involved.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
This assignment intends to discuss and evaluate the necessary health and safety policies, systems, procedures, and practices in accordance with legislative requirements as well as possible solutions and the associated dilemmas based on the case study of Silver Meadows Care Home. Three major tasks are covered in this assignment.
Firstly, the implementation of policies, systems, procedures, and practices aimed to communicate health as well as safety information; responsibilities of health and social care home management and staff in managing health and safety; as well as an analysis of appropriate health and safety priorities of case study health and social care home.
Secondly, risk assessment and the importance of obtained information in health and social care planning; analysis of a particular aspect concerned with health and safety policy; as well as dilemmas that are encountered in implementing health as well as safety policies and systems in addition to potential effect of non-compliance with legislations concerned with health and safety. Finally, the process of how to monitor and review of health aa well as safety policies, systems, procedures, and practices and their effectiveness in promoting safe culture and a healthy workplace as well as evaluation of personal contribution.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
TASK 1
Health is without any doubt the most important concern for everyone, and safety is inseparable from health service. As a result, this has been the key reason why various policies and laws have been formulated concerning health and safety with regards to health and social care working environments. Discussion of the details is presented in the sections below:
Task 1: (a) Implementation of Policies Systems, Procedures, and Practices for Communicating Information on Health and Safety
In conventional health care as well as safety settings communication usually involve various aspects, including information exchange among staff, management as well as patients and their relatives. However, due to technological advancement there has been continuous expansion of possibilities for storage, processing and retrieval of medical data.
According to Tripathi et al., (2009) varied types of information technologies and applications in the medical field have continued to enormously grow and evolve to ensure effective management and communication health as well as safety in both social and health care settings. From a perspective of social and health care workplace, there are several legislations that aim to support health and safety that are discussed below:
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
- The 2008 Act on Health and Social Care
In this Act information technology and communication (ICT) in health products are considered critical in disseminating important information concerning welfare, health and safety. This is attributable to the fact that, ICT can be used to allow control or combination of various sources of information in order to gain efficiency and provide better care within a health and safe environment while making sure that staff and resources are freed up. As a result, implementation of communication policies, systems and procedures in the Silver Meadow Care Home in accordance with this legislation will lead to various benefits, including:
Patient Safety: This is because they will result to reduction of medical errors such as surgical errors, adverse drug related admissions, transfusion errors, as well as professional negligence.
Quality of care: Health information technology (HIT) reduces paperwork and provides more time to nurses which can be used to attend to their patients (Tripathi et al., 2009). As a result, Silver Meadows Care Home residents can get quality care from the physicians, nurses and the cares due to the saved time.
Patient access to care: Access to health and social care is improved using Health information technology (HIT) by ensuring that processes that are ineffective are streamlined resulting to increased staff productivity. The indicators of success in provision of care includes: time-out results analysis, time taken to respond to patients’ inquiries, as well as improved self-management of chronic diseases.
- Health and Safety at Work Act 1974
This Act usually considers a variety of issues that are related to health, safety, as well as welfare of employees across various workplace sectors. With regards to requirements of health and safety, this Act delegate a general obligation to the management and staff of health and social care homes to cooperate and take care of others concerning issues pertaining health and safety.
- Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1992
The Act is a refinement of 1974 Act where it requires the management of health and social care homes to regularly conduct risk assessments and record findings prior to communicating them to employees and patients. This Act compels the management to arrange on implementation of health and safety measures for the purpose of improving emergency procedures as well as providing clear information and training to their staff and also work in collaboration with other stakeholders.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
- Health and Safety Regulations 1981
In order to boost health and safety, this regulation compels the management of health and social care workplace to provide information to staff, patients and visitors on first-aid arrangement. In addition, they must also ensure that there is provision of first aid equipment as well as availability of trained first aiders.
This means that it is inevitable for the implementation of health information technology in Silver Meadows Care Home to step up health and safety in its settings, which has to be carried out in accordance with the entire raft of standard, legislation, as well as guidelines altogether referred to as “Information Governance” in UK. It has been operational for sometimes and cover issues of accessing and disclosing health information as well as confidentiality.
The 2008 Act on Health and Social Care establishes the National Information Governance Board for Heath and Social Care, (NIGB) which is mandated to carry out a statutory duty of supervising the governance of information (Tripathi et al., 2009).

Figure1: Implementation Model (Source: Pall, 2012)
According to Stranks, (2005) Health Department is obliged to formulate policies regulating provision of services related to health and social care to people across UK. Even though implementation of these policies and procedure may be compromised by non-compliance, rectification can be achieved through regular monitoring by supervisory agencies shown in the above figure which ensure home cares oblige to specific health and safety policies at all levels.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Task 1: (b) Responsibilities of Management and Staff in Managing Health and Safety
Management and staffs of Silver Meadows Care Home just like those in other home care settings have certain responsibilities that they are supposed to adhere to. Elderly people are without any doubt the most vulnerable age group of the population implying that special consideration must be taken towards their safety, care, and security (Fisher, 2005).
According to Sowers & Catherine (2008) all the staff of elderly home care must be able to readily access up to date policies for nursing care and medication guidelines. On the other hand, the British National Formulary must also be readily accessible to nurses working at Silver Meadows Care Home.
In the UK, planning of health and safety in health as well as social care workplaces is conducted by both non-government institutions as well as government institutions. There exists a public health and health care system in the government of UK. In this system, there is distribution of responsibilities from the department of health down to the local authorities. As a result, the system includes health and social care providers and takers,
NHS commissioning board, clinical commissioning board, monitoring system as well as public and local health (Pall, 2012). There is an integration of this system where responsibilities are delegated to all organisational bodies based on health and safety which ought to be provided by social and health care homes.
Management is the other crucial aspect of safety and health with regards to organisational structure, particularly in relation to the management and staff responsibilities at health and social care home. In the management of health and safety responsibilities of management as well as staff include: systemic utilisation of standardised techniques which are important in the identification and removal of impeding hazards; and controlling potential risks by influencing behaviours as well as encouraging attitudes during techniques (Pall, 2012).
As a result, the responsibilities of management and staff in relation to health as well as safety management at Silver Meadows Care Home can be assessed in the context of care and support plan for a physically disabled individual because palliative care is offered.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
For example: A Care and Support Plan for a Physically Disabled Individual
Based on the care and support for the physically disabled individual, the plan includes taking the person to a restaurant once per week to take dinner since he/she is unable to this individually. However, the person wants to eat a burger at the restaurant every time when taken out, but the carers or support workers are of the opinion that burgers are not healthy and the person should not eat them that often.
Here the management and staff of Silver Meadows Care Home through their responsibilities with regards to management of health and safety can devise individualised mental capacity for making a better decision. But within the responsibilities of management and staff is it a good decision to hinder such a person to take fatty foods? From this perspective, the answer is yes; however, they should ensure that they use in supporting and encouraging tone of voice so that they feel as though they are being bullied.
They should also concern them in taking responsibility when they eat foods that are unhealthy. This implies that responsibilities and management of health and safety are related to individuals as well as the organisation. Furthermore, the example of care and support plan provided shows how the management of health and safety can be comprised and the appropriate steps that can be used to rectify it also discussed.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Task 1: (c) Analysis of Health and Safety Priorities
Care homes should be maintained in a manner that portrays a home in order to be pleasant to live in by providing safe and healthy environment. Hence, the management and staffs of care homes should prioritise the most important issues with regards to maintaining high quality health and social care for the residents.
In the context of Silver Meadows Care Home, which offers dementia care, palliative care, nursing care, and residential care for the elderly people, it is clear that there should be some appropriate health and safety priorities. For instance, since Silver Meadows is taking care of elderly people whose movement is limited there is need to prioritise the safety of entry and exit in the workplace to allow easier movement in case of an emergency (Moonie, 2000; Sprenger, 2003).
Also considering that elderly people are not stable and vulnerable to fallings, the floors should always be maintained in good state and not wet or slippery through better housekeeping practices (Sprenger, 2003). In health and social care settings, infection is the main risk and its prevention should be prioritised since elderly people often have compromised immune systems meaning new infections or cross infections may pose a significant danger to them.
This can be controlled by limiting the number of visitors or employees to an area considered risky; using measures of hygiene which reduces or prevents transferring of infectious agent through regular hand washing and ensuring that the work environment is maintained in a hygienic condition. Reducing the risk of sharp injuries should also be prioritised at care home through engineering controls and elimination of risks as well as safe usage and disposal of sharp objects (Sprenger, 2003).
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Task 2
In order to understand the impact of requirements of health as well as safety on practitioners and customers of health and social care homes, there is need to carry out risk assessment, as well as impacts of policy on customer and care practice, care planning, encountered dilemmas, as well as effects of non-compliance. Details of these aspects are discussed in the contents that follow:
Task 2: (a) Risk Assessments’ Information and Care Planning for Residents
Information on the services offered by health and social care home constitutes an important element of ensuring services are provided and taken in the context of health and safety in care planning. This can either be in the context of organisational decision making as well as individual care planning.
Risk assessment is the most appropriate method to collect this information because it involves identification of impending hazards, possible severity of harm likely to result from of the identified hazards, calculating the extent of risk, monitoring as well as reappraisal of the risk (Grinnell & Yvonne, 2008). Hence, there is need for regular risk assessments in order to assess the risks associated with health and safety of individual care planning.
In most instances, the nature of risk assessments tend to be simple and can be done through direct observation/examination, but some are more complex and requires lengthy procedures to ascertain. The process of risk assessment involves several steps which have to be executed as follows:
(1) significant hazards are identified through observations or interviews;
(2) making a decision on who is likely to be harmed by the hazards;
(3) evaluating the risks and deciding on the effectiveness of existing precautionary measures followed by implementation of proper measures if the existing ones are ineffective;
(4) recording the findings and communing them to the staffs; and
(5) reviewing the risk assessment and if necessary revisiting it (Lishman, 2007). The model of risk assessment in health as well as safety management is illustrated in the figure below:
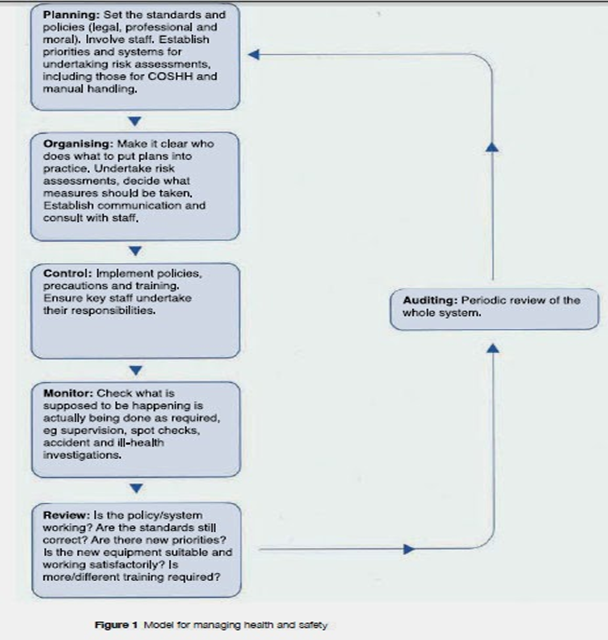
Figure 2: Model for managing health and safety in work place, (Source: Dowding & Barr, 1999)
The information obtained from risk assessments plays a critical role in informing care planning for residents and organisational decision making concerning policies and procedures because its inherent features which include: it is recognised as a risk control, its implementation is done in accordance with modern procedures to manage risk, the risk assessment needs to be reviewed and revisited or amended if necessary, it ensures that there is control of all hazards, and it results in mitigation of any residual risk to be reasonably practicable.
According to Carr (2010) getting information from risk assessments can be of considerable benefits; for example, at individual care planning they include: knowing different care services offered by various health and social care facilities, knowing better providers of health and social care, knowing the rights of getting the services of health and social care homes, appraising services offered by health and social care homes, as well as helping to make decisions on services to be sought.
In addition, in the context of organisational decision making benefits include: an organisation gets to be aware of different procedures policies that concern social and health care, an organisation can get to be aware of new procedures and policies concerning health as well as safety management at care homes, it helps an organisation to decide on the services to give to a client and how to give, and also the information helps organisations to be conscious with regards to their right, client right as well as obligations (Carr, 2010).
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Task 2: (b) Analysis of a Particular Aspect of Health and Safety Policy
In UK, various health and safety policies do exist with regards to regulation of different aspects of health and social care settings. There are both positive and negative impacts of these policies. One of safety and health policy is the Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1992. This regulation is the basis of the policy made against aggression and violence in care homes and has varied impacts care home service users and the care providers (OSHA, 2012).
This is because aggression or violence expressed by some service users is a source of distress and injury to care providers at work. This policy helps in reducing aggression and violence which positively impact the care providers. Alternatively, it may hinder health care provision to service users with aggressive or violent behaviours, especially those seeking dementia care due to their limited cognitive ability. The policy also causes financial burden to care providers since they have to continuously train their staff on how to effectively handle patients who are potentially aggressive or violent.
Another policy is Health and Safety Regulations 1981 which compels the management of health and social care workplace to provide information to staff, patients and visitors on first-aid arrangement as well as ensuring that there is provision of first-aid equipment and presence of trained first aiders (AHS, 2010).
This policy helps care providers or other patients to immediately get first when injured by violent patients or from any other accidents. However, it increases cost of running care home in purchasing first aid equipment and recruiting first aiders. Both policies seem to have both positive and negative impacts, but it is also clear that their overall impact is good to care providers and patients even though they may hinder service provision (Balarajan et al., 2011).
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Task 2: (c) Addressing Dilemmas Encountered Implementing Systems and Policies for Health, Safety and Security
Silver Meadows Care Home is faced with dilemmas in ensuring that every legislation is adhered to because of their budgetary implications as well as quality care improvement or staff performance and also security measures. Popple & Leslie (2008) asserted that based on required expectations and stakeholder needs implementation of necessary systems is needed with emphasis on government requirements. Dilemmas are the concerns the facility face to ensure security and safety of patients is guaranteed (Popple & Leslie, 2008).
Thus, the specific dilemmas include the need to ensure security and safety of patients always since it is the responsibility of the facility to guarantee the well-being of patients within a secure environment. In addition, budgetary requirements to implement the appropriate systems for assured security and safety of patients is another dilemma because the facility is faced by financial constraints and needs to outsource for the required capital.
Considering Silver Meadows Care Home is considerably large, there is need to maintain high security levels as well as safety processes. Through implementation of new technology for operating systems and departments, it is possible to effectively manage time and increase the quality of care. However, these dilemmas can be addressed by liaising with management through which services of consultants can be used to monitor the activities through which the performance of employees can be improved.
In order to increase the quality level of health and social care, continuous training programs need to be provided for the staff in order to ensure standards are developed. Finally, the dilemma with security can be addressed by implementing security camera system to increase safety at home care. According to Mizrahi & Larry (2008) implementation of a process of performance evaluation can maintain standards of employees with regards to Health and Safety Act 1981.
Stringent adherence to policies, legislations and codes or standards of practice is also essential in achieving this goal as well as reducing risk irrespective of investments required since through cost benefit analysis should obviously give more benefits than costs.
Task 2: (d) Effects of Non-Compliance with Health and Safety Legislation
In case, health and social care home is non-compliance with a legislation or regulation which govern health as well as safety, its performance becomes ineffective and clients are dissatisfied. This means that when standards are not maintained in a home care, clients become unhappy and often seek health care services from other providers.
According to Mathis & Jackson (2010) failure of a home care to provide the necessary training programs to their employees on existing legislation, regulations and standards often results to non-compliance subsequently hindering performance and quality service which eventually reduces the profits.
According to Rosenfeld & Russell (2012) non-compliance to legislation may result to legal actions, especially when patients’ rights are violated as a result of failure of home care to maintain the legislation or the standards. The legal actions may also incur the home care a significant financial burden in terms of compensations and legal fees.
Also, the home care may be banned to operate by the government due to gross violation of patients’ rights arising from non-compliance to legislation. Furthermore, when a home care is non-compliance with existing legislation the overall impacts may be increased risk, customer dissatisfaction, poor performance, poor levels of productivity, and a possibility of a ban from the government.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
TASK 3
Understanding of the process of monitoring and review of health as well as social care workplace policies, systems, procedures, and practices is central to success in health and safety implementation. This section covers the monitoring and review of safety and health policies, systems and practices as well as their effectiveness in the promotion of safe culture and healthy workplace as well as evaluation of personal contribution. Details of these aspects of health and safety have been discussed in the following contents:
Task 3: (a) Monitoring and Review of Health and Safety Systems, Policies, Procedure as well as Practices
Health as well as safety systems, policies, procedures, and practices monitoring plays a fundamental role in managing safety and health in home cares. However, writing and launching of health and safety policy does not mean that is the end of responsibilities. In fact, it is the initial step in implementing a safety and health policy, which is vital in ensuring the required standards and codes or procedures are outlined alongside the need to ensure that they are always adhered to by everyone.
Since there is a continuous change in safety and health management, the monitoring of the policies’ effectiveness needs to be done proactively for the purpose of regular evaluation of the progress and timely identification of deviations. Hence, monitoring and review of social and health care is required due to legal, morale as well as cost reasons. However, two general ways of monitoring as well as reviewing health and safety policies exist such as: proactive and reactive monitoring.
Proactive monitoring which involves taking precautionary actions prior to a hazard constitutes the checking of implemented standards as well as control of management needs through regular inspections in addition to safety audits. This plays an imperative role in ensuring that preventative or protective measures and interventions are developed and implemented.
As a result, this leads to significant reduction of risks as well as considerable gains in terms of costs reduction through minimised damages. Alternatively, reactive monitoring involves examination of events upon their occurrence and constitutes learned lessons from previous mistakes. Regular inspections of health and safety policy are an appropriate method of reviewing the progress of implementation.
This approach is important in ensuring that risks or damages are mitigated in a timely manner for the purpose of abating their negative effects, which if left unaddressed would result to significant liability or taint the reputation of the facility. Thus, the need for devising the correct interventions is very important for long-term impact to be felt.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Task 3: (b) Effectiveness of Safety and Health Policies, Systems, Procedures, and Practices in the Promotion of a Positive, Healthy and Safe Culture
Health as well as safety systems, policies, procedures, and practices’ effectiveness is depended on social and health care promotion by focusing on several factors such as: the promotion of non-occupational factors and healthy lifestyles, as well as the organisational environment. Non-occupational factors are: home and community conditions as well as family welfare. On this aspect, emphasis should be directed to improving home and community conditions mainly by devising an appropriate approach through which collaboration between all the concerned parties can be achieved.
Healthy lifestyles can be achieved through heightened awareness creation programs across all groups as well as encouraging change of lifestyles by highlighting the envisaged benefits. In addition, organisational environment is achievable through implementation of the necessary occupational safety and health standards as well as developing and implementing appropriate workplace designs and organisation. WHO proposed an effective model presented in the figure below:

Figure 3: Effectiveness Model of Health and Safety (Source: WHO, 2013)
The policies discussed previously such as the Management of Health and Safety at work Regulation 1992 puts more emphasis on risk assessments and reporting of findings, while Health and Safety Regulation 1981 compels home cares to provide first aid. These two policies play a critical role in promoting healthy workplaces as well as safe culture.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Conclusion
In conclusion, it is safe to state that health and safety implementation in home care, an integrated policy is required through which everyone will get surety to equity in health and social care. For the development of competence of health service providers, there is need for an integrated training since without such policy individuals will be taking their health risk responsibility.
References
AHS (2010). Strategic Plan for Workplace Health and Safety. Available at: https://:www.albertahealthservices.ca/org/ahs-org-whs-strategic-plan.pdf [Accessed 12th November 2015].
Balarajan, Y., Selvaraj, S., & Subramanian, S. V. (2011). Health care and equity in UK. London: Prentice Hall.
Cambridge Training and Development (2000). Advanced Health and Social Care, (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Chu, C., Breucker, G., Harris, N., Stitzel, A., Gan, X., Gu, X., & Dwyer, S. (2000). Health-promoting workplaces: International settings development. Health Promotion International, 15(2), 155-167.
CIS-Assessment (2010). Health and Safety in an Adult Social Care Setting. Available at: https://:www.cis-assessment.co.uk/docs/pdf [Accessed 12th November 2015].
Dean, K. (1996). Using theory to guide policy relevant health promotion research. Health Promotion International, 11(1), 19-26.
Dowding, L., & Barr, J. (1999). Managing in Health Care: A Guide for Nurses, Midwives & Health Visitors, (5th ed.). New York, NY: Prentice Hall.
Fisher, A. (2005). Health and Social Care. Oxford: Heinemann.
Garcarz, W., & Wilcock, E. (2005). Statutory and Mandatory Training in Health and Social Care: A Toolkit for Good Practice. Oxon, OX: Radcliffe Publishing.
Graham, B., & Steven, P., (2008). Your Foundation in Health and Social Care: A Guide for Foundation Degree Students. London: SAGE.
Grinnell, R. M., & Yvonne, A. U. (2008). Social Work Research and Evaluation: Foundations of Evidence-Based Practice (8th ed.). Oxford, UK; New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Grol, R., et al., (2007). Planning and Studying Improvement in Health Care: The Use of Theoretical Perspective. The Milbank Quarterly, 85(1), 93-138.
Holland, K., & Hogg, C. (2001). Cultural Awareness in Nursing and Health Care: An Introductory Text. London: Hodder Arnold.
HSE – Health and Care Services (2013). Health and Care Services, [online]. Available at: http://www.hse.gov.uk/healthservices/index.htm [Accessed 12th November 2015].
HSE – Monitor Health and Safety (2014). Monitor Health and Safety [online]. Available at: http://www.hse.gov.uk/leadership/monitor.htm [Accessed 12 November 2015].
HSE – Review Health and Safety Legislation (2014). Health and Safety Legislation – laws in the workplace [online]. Available at: http://www.hse.gov.uk/legislation/ [Accessed 12th November 2015].
HSG (2000). Managing Health and Safety on Work Experience: A Guide for Organisers.
Lishman, J. (2007). Handbook for practice learning in social work and social care: knowledge and theory. London: Jessica Kingsley.
Mathis, R. L., & Jackson, J. H. (2010). Human Resource Management. New York, NY: Cengage Learning.
Moonie, N. (2000). Advanced Health and Social Care. Oxford: Heinemann.
Morath, J. M., & Turnbull, J. E. (2004). To Do No Harm Ensuring Patient Safety in health Care Organizations. Sainsbury, NJ: Jossey Bass Wiley.
NHS (2013). NHS choices, [online]. Available from: http://www.nhs.uk/aboutNHSChoices/Pages/NHSChoicesintroduction.aspx [Accessed 12th November 2015].
Nolan, Y. (2005). Health and Social Care (Adults). Oxford: Heinemann.
Occupational Health and Safety Act (2012). Occupational Health and Safety Act [online]. Available at: http://www.e-laws.gov.on.ca/html/statutes/english/elaws_statutes_90o01_e.htm [Accessed 12th November 2015].
Pall, N. (2012). Primary healthcare needs top priority. Mumbai: India Health Progress.
Pamela, M., & David, W., (2009). First Health and Social Care, (1st ed.). London: Reflect Press.
Payne, M. (2011). Humanistic Social Work: Core Principles in Practice. Chicago: Lyceum, Basingstoke, Palgrave Macmillan.
Popple, P. R., & Leslie, L. (2008). The Policy-Based Profession: An Introduction to Social Welfare Policy Analysis for Social Workers (4th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson/Allyn and Bacon.
Reamer, F. G. (2006). Ethical Standards in Social Work: A Review of the NASW Code of Ethics, (2nd ed.). Washington, DC: NASW Press.
Rosati, R. J. (2009). Home healthcare quality. Journal of Healthcare Quality, 31(2), 3-4.
Rosenfeld, P., Pyc, L., Rosati, R. J., & Marren, J. M. (2012). Developing a Competency Tool for Home Health Care Nurse Managers. Home Health Care Management & Practice, 24(1), 5-12.
Rosenfeld, P., & Russell, D. (2012). A Review of Factors Influencing Utilization of Home and Community Based Long-Term Care: Trends and Implications to the Nursing Workforce. Policy, Politics & Nursing Practice, 13(2), 72-80.
Sowers, K. M., & Catherine, N. D. (2008).Comprehensive Handbook of Social Work and Social Welfare. Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley & Sons.
Sprenger, R. (2003). Health and Safety for Management. London: Highfield.
Stranks, J. (2005). Health and Safety Law, (5th ed.). London: Prentice Hall.
Trachtenberg, M., & Ryvicker, M. (2011). Research on transitional care: from hospital to home. Home Healthcare Nurse, 29(10), 645-651.
Tripathi, M., Delano, D., Lund, B., & Rudolph, L. (2009). Engaging patients for health information exchange. Health Affairs, 28(2), 435-443.
Webb, R., & Tossell, D. (1998). Social Issues for Carers: Towards Positive Practice, (2nd ed.). London:Hodder Arnold.
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here