Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Culture and Strategy
Abstract
The relationship of organizational culture and progression has been subject of different examinations over the span of the latest years. The colossal number of social variables under investigation has incited an isolated thought of society for development.
Further, managerial practice requires a concealed structure remembering the final objective to pick what society should be completed in order to improve and to study if a specific culture is a convincing and powerful coordination instruments. The motivation behind this paper is to inspect the idea of the hierarchical culture and give a brief discourse on the methodologies utilized for overseeing it in culture and strategy of organizations.
- Introduction
Hierarchical culture emphatically influences organization and administration, which ascend out of its slant and its substance. Hierarchical society is described as a course of action of assumptions, qualities, norms, and perspectives, appeared through pictures which the people from an organization have made and gotten through basic experience and which offer them some help with deciding the essentialness of their general surroundings and how to absorb it. (Janićijević, 2011).
Presumptions, qualities and gages which the general population from a firm shares completely shape their interpretative game plans. Through interpretative courses of action, the general populations from an association assign repercussions to events inside and outside the association and comprehend reality that incorporates them (Janićijević, 2011). The conduct, activities and trades of the general population from an association rise out of the inducing that reality of that association has for them.
Various leveled society is a sort of aggregate interpretative course of action shared by the general population from an association, because of which they dole out proposals to events, individuals, and occasions inside and outside of the association correspondingly and treat them moreover (Janićijević, 2011). In this way, the lifestyle of an organization surmises that each one of the people from the organization likewise appreciate the organization.
The character of different parts of management and organization, for instance, methodology, structure, activity style, Organizational taking in, a game plan of prizes, and motivation, rises totally from the way in which delegates and administration understand authoritative reality and carry on in it (Janićijević, 2011). Thusly, Organizational society, through its effect on the interpretative plans and direct of the people from an organization, shares in framing distinctive portions of organization and administration.
Subordinate upon the qualities and measures contained by the Organizational society, top organization picks the technique and courses of action progressive structure, boss shape their drive style, delegates depict their behavior of intuition and needs, and the human asset executive plots the pay framework in an affiliation. A solid sort of the effect of Organizational society on an association and organization is found in the way that parts of an association and organization vary in various sorts or sorts of legitimate society. By the day’s end, specific sorts of society in association’s propose different techniques, legitimate structure models, pay frameworks, organization styles, and so forth (Janićijević, 2011).
One of the key parts of organization that are impacted by definitive society is the organization of progressive society. Definitive society impacts the choice of satisfactory Organizational culture organization correspondingly it impacts every single another bit of organization. Social suppositions and qualities shared by the general population from an association pick the path in which workers and executives will value the association itself, and thusly the satisfactory approach to manage transform it (Janićijević, 2011).
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
What will be resolved as a suitable, effective, or steady methodology for changing the association will rely on upon an exceptionally fundamental level on the common suppositions and estimations of operators and managers worked in their interpretative game plans. Whether the developments are incremental or radical, complete or deficient, encouraged starting from the top or from the base up, concentrated on the culture of the “hard” or of the “touchy” some segment of association, will all, metaphorically talking, rely on upon how the pioneer and the general population from the association see its working and a suitable, strong, or down to earth method for taking off improvements (Aguiree, Post, and Alpern, 2013).
This is the motivation driving why the strategy of legitimate culture organization will be all around assorted in various Organizational social requests. For instance, if various leveled society is told by the estimation of adaptability, this recommends the general population from the association will consider cultures to something unprecedented and obliging for the association and themselves.
For this situation, cultures are slanted to be reliable, and thusly additionally incremental in nature, in light of the way that there will be no need for radical cultures adequately by virtue of the way that they are consistent (Janićijević, 2011). Additionally, cultures will be driven with less resistance yet rather more eagerness by the agents. Then again, if Organizational society contains the estimations of predictable quality and conservatism, then the general population from the association will consider cultures as dangerous, both for themselves and the association.
Cultures will be phenomenal, yet when they do happen they will be radical and wide. They will be composed to a wonderful level of resistance from and an all around insignificant level of sponsorship by the general population from the association, who will be for the most part sit out of gear powers of progression (Janićijević, 2011).The degree of this paper is to appreciate and examine the legitimate society and organization philosophies to manage the troubles stood up to by the various affiliations.
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
- Review of Strategies for Organizational Culture
In the extent of various leveled culture association, the considered scholastic specialists and honing boss has been basically focused on three central solicitation: what cultures, why it cultures, and when it cultures. Along these lines, the three key subjects in various leveled culture research have been causes or variables of legitimate culture, definitive culture content, and the character of the progressive culture process.
The conclusion came to has been that authoritative cultures are begun as a result of either internal or external causes. From this time forward, two sorts of hierarchical culture have been isolated by the measure of cause: authoritative headway and alteration (Aguiree, Post, and Alpern, 2013).
Concerning culture content, the survey of forming demonstrates that progressive cultures are segregated in two imperative courses: cultures of definitive statics (structure and framework) and cultures of legitimate segments (process), besides cultures of work structure (assignments) and cultures of social structure (relations)). At long last, research has displayed that, as showed by the character of the strategy, various leveled cultures can be tireless or sporadic.
Tenacious cultures are incremental (first request cultures), divided, and transformative while sporadic cultures are radical (second request cultures), complete, and dynamic. The part of the pioneer in the midst of the time spent culture has moreover been a fundamental issue in definitive culture research (McGuire, 2003; Madu, 2005).
Not at all like the issues of cause, substance, have process, and authoritative culture organization, hierarchical culture methods been less present in investigation. Authoritative culture framework joins the system, strategy, or route in which cultures are realized in an affiliation. This definition proposes that movements are continually orchestrated and that, at whatever point we examine culture execution method, we truly discuss masterminded hierarchical cultures (McGuire, 2003; Madu, 2005).
The way that the primary course of action of authoritative culture strategy oversees organized culture system in like manner adds to this impression. In any case, this does not for the most part should be the circumstance. Cultures can similarly be unconstrained or unconstrained, and their anticipated approach, strategy, or the best approach to constitute a culture framework. They can be a strategy for recognizing authoritative culture, regardless of the way that the movements are off the cuff (McGuire, 2003; Madu, 2005).
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
While most specialists while examining business or corporate approach truly mean adjusted, formalized, organized decisions, distinctive scientists point out that strategy, can rather be fathomed as a bona fide security partner particular business decisions and giving them consistency, which is new and just thusly legitimized as a framework, rather than a normal, orchestrated decision arranged early (McGuire, 2003).
Likewise, in the field of hierarchical culture, culture framework may be fathomed as a masterminded decision of the administrators of advancement, furthermore as a creating case of development through which cultures are recognized and which grabs its shape entirely when the movements have been made sense of it. Starting now and into the foreseeable future, the discernment of legitimate society structure in this paper is to some degree more wide than the one in the much grasped work by Chin and Benne, who were the first to accumulate progressive society frameworks (McGuire, 2003).
The judicious observational system is developed on the suspicion of the common sense of Organizations and the comprehensive group who constitute them (Sami, 2012). Affiliations are seen as a shrewd means for completing the common focuses of their kin through aggregate activity. Individuals are overseen as regular creatures lead with no other individual’s data interest.
Along these lines, societies are executed by demonstrating the general population from an association that they are reasonable, i.e., reinforced and critical from the viewpoint of accomplishing progressive objectives, furthermore obliging to the self-vitality of the general population from the alliance (Sami, 2012). The supposition is that the general population from the relationship in which the developments are performed will, as normal creatures, carry on as exhibited by their reasonable given side hobbies.
Therefore, in the event that they are given watch that a society is to their most essential purpose of inclination, they will remember it.Cultures are driven through the typical system of information party and utilization of learning in dealing with the issues that the affiliation faces. Essentially, cultures are driven through the methodology of utilization and testing of specific theories, which give off an impression of being adequate in a given setting (Long, 1997).
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
Authoritative cultures are driven in five stages: issue conspicuous verification, information get-together and examination, the time of alternative diagrams, determination of the perfect procedure, and execution of the game plan. In the adjusted framework, the key driver of societies is accurately the data with respect to the issue which should be taken care of and the conceivable fundamental reasoning strategies.
On the off chance that the data is instigating and clear, and on the off chance that it is decisively in all actuality, the general population from an association will, as shrewd creatures, perceive the execution of societies (Luthans, and Doh 2008; McGuire 2003). It is thusly vital that data gathering is driven purposefully and in a methodologically noteworthy way, ideally by an authority (it is as regularly as could reasonably be expected the case that advice are contracted in this way).
The strategy of granting information concerning the issue and with respect to the movements which will deal with the issue is uneven and beginning from the top. Correspondence includes top organization, or authorities picked by top organization, showing the “truths” of the bona fide condition, the theoretical model which enables the offered situation to be understood ‘legitimately’, and also the proposition for culture which really ascend out of this perception (Luthans, and Doh 2008; McGuire 2003).
No dialog or talk is joined into which the people from the affiliation would be allowed to test, address, or rename the “truths” or theoretical models showed to them (Luthans, and Doh 2008; McGuire 2003).
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
It is clear that the executives of headway in this system are the top association, and that the heading of progression is starting from the top. The part of the general population from the connection is sit without moving and is obliged to enduring the data and acting in like way. The level of support of the alliance individuals is low, and the response to this course of action of the people in the developments is, most perfect circumstance, assertion. As a last resort, the imperviousness to culture is high (Luthans, and Doh 2008; McGuire 2003).
- Leadership/Management and Organizational Culture
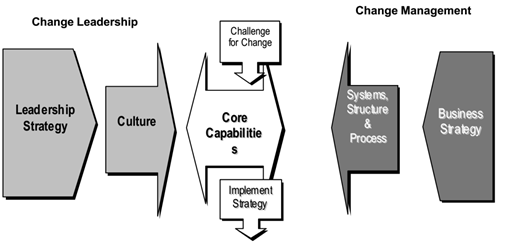
Organizations are not any more liable to accomplish business objectives without a key business process that are associations liable to accomplish new social abilities without a key authority process. Whenever consolidated, the business methodology and authority system can work all the while to grow new center capacities essential for the association’s future.
We present the defense that it is administration, as a deliberate gathering of similarly invested individuals, which can exhibit and take part in the better approaches for doing and being that advances the way of life and empowers diverse business results (Dilobe &Haccoun, 2010; House, Javidan, Hanges, & Dorfman, 2002; Eromafuru 2013; Woszczyna , 2011; Salamzadeh, , Ahmadi & Akbari, 2012; Eromafuru, 2013).
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
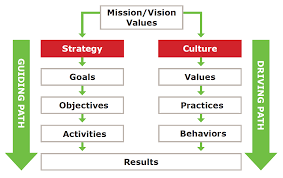
It is an initiative that imagines future course, adjusts assets, and rouses the dedication of individuals toward this normal reason. A Leadership Strategy can control that basic procedure of the association’s advancement through initiative toward a typical reason for building the couple of, new capacities inside of the heart of the association – its way of life. Adjusting to culture recommends that associations need go to new center capabilities. The movement from an item prompted administrations drove IBM required that the way of life of this once ambling behemoth turn into a group based, the client engaged, elegant organization (McGuire, 2003).
Figure: Leadership Strategy McGuire (2003).
According to Haccoun et.al, (2010); Dorfman et.al, (2002); Eromafuru (2013); Woszczyna , (2011); Akbari et. al, (2012); Eromafuru, (2013), the key mechanical assemblies for executing society in perceiving observational procedure are assignments, or work positions, and not the social structure of the affiliation and the relations within it. Consequent to the affiliation is appreciated as a prudent contraption for achieving shared targets, societies in it are recognized fundamentally through changing the formal, masterminded, “hard” parts: endeavors, structures, methods, methodologies, strategies, and the association with its environment.
Simply first demand societies can be instated and coordinated through the sound observational system since the method does not allow renaming of the assumptions of reality; this future a bit of second demand societies. As a rule, societies don’t require all that much time; beside when the information gathering technique is greatly mind boggling (McGuire, 2003).
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
A deterministic, as opposed to the voluntary supposition of human activity, underlines this technique. The procedure of progress does exclude the through and through freedom and decision of individuals from the association. The strategy, or of progress, is as of now dictated by the target way of the issue, and it is the undertaking of the individuals who settle on choices in the association simply to apply it to sufficient information and hypothesis (Dorfman et.al, 2002; Eromafuru, 2013).
Power coercive strategy translates that a connection is seen as a political structure in which the general population who have the force likewise have the advantage to deal with the association and along these lines change it. The man is not a run of the mill but rather a political being, who submits to the will of the all the more compelling. Along these lines in force coercive framework force is the key driver and contraption for society (Dorfman et.al, 2002; Eromafuru, 2013).
The general population who have the force; when in doubt the pioneer or top association, coordinate the developments and, by mauling the force they have, power these developments on interculture individuals from the connection. The general population from the alliance is relied on to obey and execute the developments unquestioningly. This strategy depends on upon the supposition that the advantage to urge the course of aggregate activity in one party in like way climbs up out of force. Along these lines, the sub-par individuals from a social event in like way anticipate that the pervasive individuals will set the course in which the developments will be executed (McGuire, 2003).
The correspondence is one-sided and coordinated starting from the top. It comprises of the pioneer or administration achieving a choice with respect to the tackling of an issue, and after that conveying to their devotees and association individuals how, when, where, and who will execute the progressions which will take care of the issue. The main operators of progress are the pioneer or administration of the association who has the ability to execute the progressions.
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
The interest of the individuals from the association in culture is low, and their part is uninvolved and boils down to minor dutifulness. In this methodology, the data stream course is starting from the top, in light of the fact that the specialists of progress just advises the association individuals from what is anticipated from them and does not get input. For the same reason, the culture exercises are one-sided (Dorfman et.al, 2002; Eromafuru, 2013; McGurie, 2005).
The power-coercive methodology can deliver just first request culture since it does exclude changing the suppositions, qualities, or states of mind of the individuals from an association. The pioneer who applies this culture system is not keen on changing the convictions and estimations of the individuals from the association so they acknowledge the progressions; rather, the pioneer, by the utilization of force, just drives them to consistence.
This is the reason the progressions will be conceivable just inside of the current worth structure, which prompts first request cultures. Of the considerable number of systems, force coercive procedure prompts the quickest results and this is its primary leverage and the motivation behind why it is utilized generally regularly. In any case, its inconveniences are exceptionally various; for instance, the decimation of inspiration and dedication, extremely solid imperviousness to cultures, and the absence of comprehension of cultures prompting their wasteful usage (Dorfman et.al, 2002; Eromafuru, 2013; McGurie, 2005).
They all Dorfman et.al, (2002); Eromafuru, (2013); McGurie, 2005) concur this society strategy is centered around relations and social structure, as opposed to on work structure and assignments. Since reliance relations are the establishment of this framework, it commonly relies on upon the relations between the effective overseers of societies and the humble individuals from the association. Therefore, control coercive strategy depends on upon relations and the social, nice, “delicate” segment of relationship as an instrument for society.
Power coercive strategy translates the viewpoint of human activity as unshakable, compelling a perspective of the world in which individuals are free directors who can independently pick their activities. In any case, this totally adaptability infers just to the capable pioneer or chief and not to the straggling remains of the alliance (Dorfman et.al, 2002; Eromafuru, 2013; McGurie, 2005)…
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
The developments are driven by first changing the suppositions, qualities, standards, and viewpoints shared by the association individuals, and after that besides changing their activities and correspondences, or relations. Along these lines, it is unequivocally these relations and social segments of the alliance that are the vital instruments of headway in regularizing re-educative framework, and not its “hard” parts, i.e. tries.
In this structure, societies happen at the level of relations between the connection individuals. Standardizing re-educative methodology merges the system of reframing, or changing, the socially-made picture of reality, from which societies of both aggregate suppositions and qualities rise (Dorfman et.al, 2002; Eromafuru, 2013; McGurie, 2005).
By researchers, Dorfman et.al, (2002); Eromafuru, (2013); McGurie, (2005); Akbari et. al, (2012); in this manner societies in this reasoning are created both starting from the top and from the base up, and the data stream is multilateral. In the standardizing re-educative structure, the managers of headway in a connection are both the association and the authorities. The alliance individuals are dynamic people in society with an irregular state of endeavor: from this time forward the solidness to culture is sensibly low.
Societies composed by regularizing re-educative philosophy assemble the dedication of the association individuals to the new picture of reality and new connection and is of a higher quality than the past two strategies which request the alliance individuals’ insistence and detached assent. The regularizing re-educative methodology might start and induce second request society since it determines changing the path in which the general population from an alliance handles their general surroundings. However the execution of this strategy takes longer, as creating suspicions, qualities, gages, and dispositions is not a quick technique.
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
- Conclusion
The paper has demonstrated that there is a theoretical explanation behind the supposition that various leveled society is one of the variables in the determination of authentic society association systems. In a split second it is the key to correctly test this presumption by testing the speculations made in this paper. It is also fundamental to look at it and how the way of life impacts the ability of the way of life framework and its flourishing. From this paper, a supposition additionally develops that there might be a criticism impact of organization society strategy on various leveled society.
Inside and out that truly matters, this paper can be prescribed to affiliation association which is planning progressive societies, to help with picking the association strategy for society that is awesome with the way of life of their affiliation. This will add to the suitability and accomplishment of the way of life procedure. With the target this should be conceivable they should have an OK learning of the way of life of the connection they are changing, besides of the open organization society procedures.
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here
References
Aguiree, D., Post, R. V., & Alpern, M. (2013). Culture’s role in enabling organizational culture. Booz & Company.
Dilobe, N., & Haccoun, R. (2010). Measuring Core Dimension of Organizational Culture: A Review of Research and Development of New Instrument. University De Catholique.
Divan, S. M. (2012). CHANGING “THE WAY WE DO THINS” (Unpublished doctoral dissertation). California State University, Sacramento, LA.
Donell, O., & Boyle, R. (2008). Understanding and Managing Organizational Culture. Dublin, Ireland: IPA.
Eromafuru, E. (2013). Building and Sustaining Organizational Culture through Innovative and Strategic Leadership. International Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 3(11).
Heracleous, L., & Langham, B. (1996). Strategic culture and organizational culture at hay management consultants. Long Range Planning, 29(4), 485-494. doi:10.1016/0024-6301(96)00040-4
House, R., Javidan, M., Hanges, P., & Dorfman, P. (2002). Understanding cultures and implicit leadership theories across the globe: an introduction to project GLOBE. Journal of World Business, 37(1), 3-10. doi:10.1016/s1090-9516(01)00069-4
Huiri, D. (2011). THE IMPORTANCE OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT. SAVONIA UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES.
Janićijević, N. (n.d.). THE INFLUENCE OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE ON ORGANIZATIONAL PREFERENCES TOWARDS THE CHOICE OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE STRATEGY. ECONOMIC ANNALS, 18(193).
Long, D. D. (1997). Building the Knowledge Based Organizations: How Culture Drives Knowledge Behaviors. Center for Business Innovation.
Lunenberg, F. (2011). Understanding Organizational Culture: A Key Leadership Asset.National Forum of Educational Administration and Supervision Journal, 29(4). Retrieved from http://faculty.mu.edu.sa/public/uploads/1360754959.415organizational%20cult63.pdf
Luthans, F., & Doh, J. P. (2008). International Managment (9th ed.). McGraw Hill.
Madu, B. C. (2005). Organizational culture as a driver of competitive advanatage. Journal of Academic and Business Ethics, 3(2). Retrieved from http://www.aabri.com/manuscripts/11791.pdf
McGuire, J. (2003). Leadership Strategies for Culture Culture Developing Culture Leadership as an Organizational Core Capability. The Center for Creative Leadership – Friends of the Center Leadership Conference, Florida.
Pudelko, M., Reiche, B. S., & Carr, C. (2011). WHY INTERNATIONAL STRATEGY AND CROSS-CULTURAL MANAGEMENT MATTERS IN BUSINESS RESEARCH AND EDUCATION. Schmalenbach Business Review.
Salamzadeh, Y., Ahmadi, A. A., & Akbari, J. (2012). Relationship between Organizational Culture and Strategy Implementation: Typologies and Dimensions. Global Business and Management Research: An International Journal, 4(3).
Sami, W. (2012, November). Organizational Culture. Helbing and Associates, 2-8.
Sliwa, M. (2011). Strategies for Culture. Culture for Development (3). mik.
Trompenaars, F. (1996). Resolving International Conflict: Culture and Business Strategy.Business Strategy Review, 7(3), 51-68. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8616.1996.tb00132.x
Tsai, Y. (2011). Relationship between Organizational Culture, Leadership Behavior and Job Satisfaction. Retrieved from BMC Health Services Research website: http://download.springer.com/static/pdf/576/
Woszczyna K. (n.d.). THE IMPORTANCE OF ORGANIZATIONAL CULTURE FOR INNOVATION IN THE COMPANY. Scientia Oeconomia, 2(3). Retrieved from http://www.wsb.edu.pl/container/Wydawnictwo/Do%20pobrania/szczepanska-woszczyna-m.pdf
Culture and Strategy
Want help to write your Essay or Assignments? Click here